Researchers from the University of Leeds are studying how to make electricity from electrodes coated in bacteria, and other living cells, using light or hydrogen as the fuel.
The aim of the research long-term is to develop more efficient biofuel cells, seen as the future of electronics. Because biofuel cells are powered by readily available biological materials, they have the potential to be used indefinitely when electricity is required at places where is it not possible to replace a battery or recharge them.
Most biofuel cells create electricity using enzymes that process glucose, but the Leeds research will focus on bacterial enzymes that can harness light or hydrogen gas to create energy. The work is funded by a £1.42m grant from the European Research Council.
Lead researcher, Dr Lars Jeuken, from the University's Faculty of Biological Sciences, says: "Technology that creates an electrical signal from a biochemical reaction is already in commercial use, for example in blood glucose biosensors. However, developing an efficient biofuel cell that can create sufficient electricity for general use has proved much more difficult. This is mainly because the systems developed to date have only limited control of how inorganic materials and biological molecules interact.
"Our research combines state of-the-art surface physics, colloid and organic chemistry, membrane biology and electrochemistry to develop electrodes with complete control of the biochemical interactions needed to create electricity. We now want to apply this to membrane proteins to generate energy from light and hydrogen."
In their simplest form, biofuel cells have two electrodes, one which removes electrons from a fuel - for instance glucose or hydrogen - whilst the other donates electrons to molecules of oxygen, making water. When these are connected by a wire, they form a circuit, resulting in an electrical current.
Dr Jeuken and his team have extensive experience in making electrodes that directly interact with enzymes located in the membranes that surround cells. This new project will begin by applying this technique to two specific groups of enzymes, one which harnesses light and the other, hydrogen. These are found in membranes of chloroplast - the parts of cells which conduct photosynthesis - or bacterial cells, both of which have promising applications in biofuel cells. The final part of the project will aim to connect electrodes to the membranes of living bacterial cells.
"Not only will this help scientists understand the role of different enzymes in making energy, but how best to capture and use this energy in electrical applications," says Dr Jeuken.
Dr Jeuken's research will also contribute to a new Interdisciplinary Centre for Microbial Fuel Cells (ICMFC), set up jointly between the Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York. The Centre will bring together chemists from York, biophysicists such as Dr Jeuken from Leeds and engineers from Sheffield, to work together on improving the performance of microbial fuel cells, using a combination of synthetic biology and nanoengineering.
Image information and credits
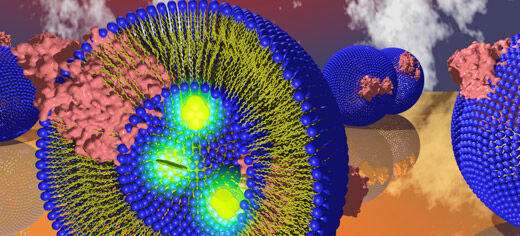
An artistic representation of submicron lipid vesicles filled with fluorescent molecules. The vesicles contain enzymes which convert oxygen to water and transport protons outside the vesicles in the process. The proton transport changes the pH inside the vesicles, which is seen by a change in fluorescence.
Credit: Image reproduced by permission of Lars J C Jeuken and The Royal Society of Chemistry from Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 49-52, DOI: 10.1039/C0SM01016B
For further information, please contact:
Contact: University of Leeds Communications & Press Office: Tel +44 (0)113 343 4031, email pressoffice@leeds.ac.uk
Notes to editors:- The Faculty of Biological Sciences at the University of Leeds is one of the largest in the UK, with over 110 academic staff and over 400 postdoctoral fellows and postgraduate students.
The Faculty is ranked 4th in the UK (Nature Journal, 457 (2009) doi:10.1038/457013a) based on results of the 2008 Research Assessment Exercise (RAE). The RAE feedback noted that "virtually all outputs were assessed as being recognized internationally, with many (60%) being internationally excellent or world-leading" in quality. The Faculty's research grant portfolio totals some £53M and funders include charities, research councils, the European Union and industry. http://www.fbs.leeds.ac.uk/ - The 2008 Research Assessment Exercise showed the University of Leeds to be the UK's eighth biggest research powerhouse. The University is one of the largest higher education institutions in the UK and a member of the Russell Group of research-intensive universities. The University's vision is to secure a place among the world's top 50 by 2015.
- The University of Leeds is acclaimed for the quality of its teaching and research. One of the largest universities in the UK, Leeds is also the most popular among students applying for undergraduate courses. An emphasis on innovative research and investment in high-quality facilities and first-rate infrastructure means that no fewer than 35 departments are rated internationally or nationally 'excellent'.