New C.diff treatment reduces recurrent infections by 40%
A new treatment for Clostridium difficile (C.diff) reduces recurrent infections by nearly 40%, a large study has found.

A new treatment for Clostridium difficile (C.diff) reduces recurrent infections by nearly 40%, a large study has found.

Restricting the use of a common antibiotic was more important than a high profile 'deep clean' of hospitals in massively reducing UK antibiotic resistant Clostridium difficile, a major study found.

A new £6.8m medical imaging centre which aims to transform the diagnosis and treatment of patients suffering from cancer, heart disease and musculoskeletal diseases has opened.
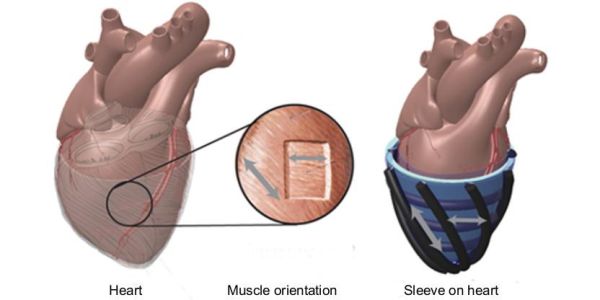
A prototype robotic sleeve, which can wrap around a weak heart before synchronising with its natural motion to help it keep beating, has been developed by an international team of engineers.

More than 200 scientists have signed up to a tissue-sharing database designed to reduce the number of animals needed for biomedical research.

A drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis can reduce the risk of heart attacks in such patients by nearly 40%, a new study has found.

Targeting a specific DNA-repairing protein in the brain could be an effective way to treat the most aggressive type of brain tumour, a study suggests.

The first woman to have an ovary frozen before the onset of puberty has given birth to a baby boy.
Women taking tamoxifen to prevent breast cancer may be stopping their treatment because of a mistaken belief it is causing certain side-effects, a study suggests.

A virus that causes childhood coughs and colds could help in the fight against primary liver cancer.