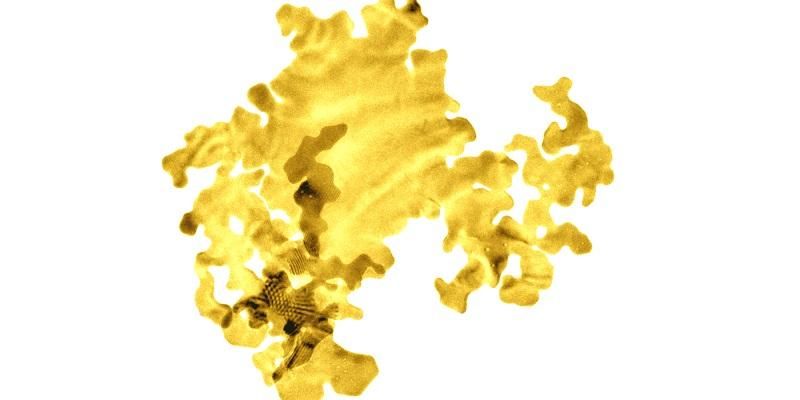

Scientists at the University of Leeds have created a new form of gold which is just two atoms thick – the thinnest unsupported gold ever created.
The researchers measured the thickness of the gold to be 0.47 nanometres – one million times thinner than a human finger nail.
The material is regarded as 2D because it comprises just two layers of atoms sitting on top of one another. All atoms are surface atoms, there are no 'bulk' atoms hidden beneath the surface.
It could have wide-scale applications in the medical device and electronics industries, and also as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions in a range of industrial processes.
Laboratory tests show that the ultra-thin gold is 10 times more efficient as a catalytic substrate than the larger gold nanoparticles currently used in industry.
'Landmark achievement'
Scientists believe the new material could also form the basis of artificial enzymes for potential use in rapid, point-of-care medical diagnostic tests and in water purification systems.
The announcement that the ultra-thin metal had been successfully synthesised was made in Advanced Science.
The journal paper's lead author, Dr Sunjie Ye, from Leeds' Molecular and Nanoscale Physics Group and the Leeds Institute of Medical Research, said: "This work amounts to a landmark achievement.
"Not only does it open up the possibility that gold can be used more efficiently in existing technologies, it is providing a route which would allow material scientists to develop other 2D metals.
"This method could innovate nanomaterial manufacturing."
The research team is looking to work with industry on ways of scaling-up the process.
Read more about the background to the research: The scientists with the Midas touch.
“...industry could get the same effect from using a smaller amount of gold, and this has economic advantages...”
Synthesising the gold nanosheet takes place in an aqueous solution and starts with chloroauric acid, an inorganic substance that contains gold. It is reduced to its metallic form in the presence of a "confinement agent" - a chemical that encourages the gold to form as a sheet just two atoms thick.
Because of the gold's nanoscale dimensions, it appears green in water, and given its frond-like shape, the researchers describe it as gold nanoseaweed.
Images taken from an electron microscope reveal the way the gold atoms have formed into a highly organised lattice structure.
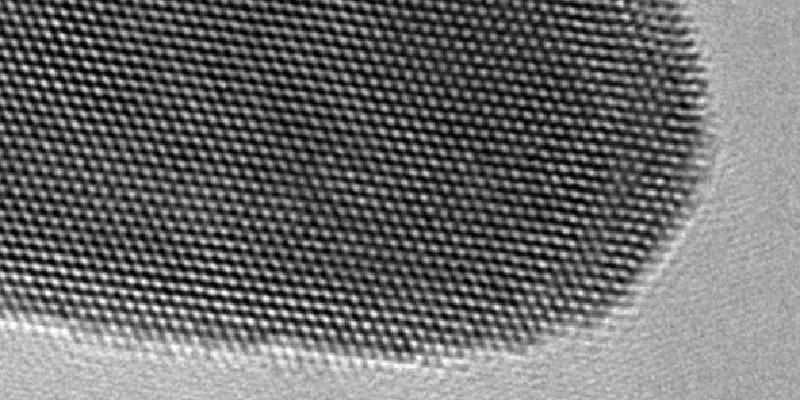
This electron microscope picture shows the gold atoms' lattice structure
Professor Stephen Evans heads the Leeds' Molecular and Nanoscale Research Group and supervised the research. He said the considerable gains that could be achieved from using ultra-thin gold sheets were down to their high surface-area-to-volume ratio.
"Gold is a highly effective catalyst. Because the nanosheets are so thin, just about every gold atom plays a part in the catalysis. It means the process is highly efficient.
"Our data suggests that industry could get the same effect from using a smaller amount of gold, and this has economic advantages when you are talking about a precious metal."
The flakes are also flexible, meaning they could form the basis of electronic components for bendable screens, electronic inks and transparent conducting displays.
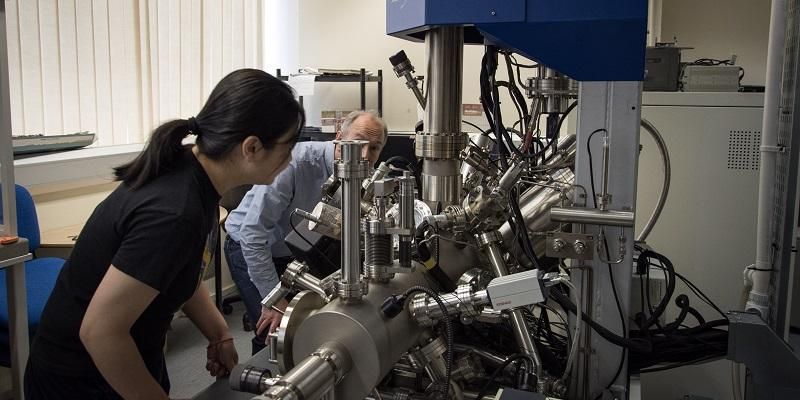
Dr Sunjie Ye and Professor Stephen Evans used x-ray photo electron spectroscopy to confirm the purity of the new form of gold
Professor Evans thinks there will inevitably be comparisons made between the 2D gold and the first 2D material ever created – graphene, which was fabricated at the University of Manchester in 2004.
He said: "The translation of any new material into working products can take a long time and you can't force it to do everything you might like to. With graphene, people have thought that it could be good for electronics or for transparent coatings, or as carbon nanotubes that could make an elevator to take us into space because of its super strength.
"I think with 2D gold we have got some very definite ideas about where it could be used, particularly in catalytic reactions and enzymatic reactions. We know it will be more effective than existing technologies – so we have something that we believe people will be interested in developing with us."
The University of Leeds is recognised for its research in material science. It runs the Bragg Centre, where academics from a range of disciplines collaborate. The centre has access to some of the best facilities in the world.
Further information
For further information please contact David Lewis in the University of Leeds press office on +44(0)113 343 2049 or d.lewis@leeds.ac.uk.