Research from the University of Leeds and an international team of scientists has shown a recent increase in atmospheric hydrogen chloride (HCl), a substance linked to destruction of the ozone layer.
It was anticipated that there would be a decline in HCl under the Montreal Protocol, the international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of ozone-depleting substances.
Dr Emmanuel Mahieu from the University of Lií¨ge in Belgium, who led the research, explained: “It’s important to say that the Montreal Protocol is still on track, and that this is a transient reversal in the decline of HCl, which can be explained through a change in atmospheric circulation, rather than rogue emissions of ozone-depleting substances.”
The study, published today in the journal Nature, explains that the unexpected increase is caused by a temporary but prolonged anomaly in atmospheric circulation, changing the balance between chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and their breakdown product HCl.
Professor Martyn Chipperfield from the School of Earth and Environment at the University of Leeds, who led the modelling work for the study, said: “The expected deterioration of ozone-destroying chemicals in the atmosphere is certainly more complex than we had imagined. Rather than a steady decline, these findings have presented a rather more complicated picture.
“Through comparison with detailed computer models, we have identified this decline as temporary due to changes in upper atmospheric wind patterns, so we remain optimistic that the ozone layer will recover during the second half of the century.”
The recent increase in HCl concentrations was only observed in the Northern Hemisphere, whilst in the Southern Hemisphere HCl continues to decrease, as expected, in line with the Montreal Protocol.
Professor Chipperfield added: “There are natural differences in the atmosphere between the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, due to the influence of the Earth’s surface topography and slight variations in the Earth’s orbit around the Sun during the year. While atmospheric chlorine levels remain high we may see cases of large ozone depletion, especially over the polar regions”.
The findings are based on measurements by a network with stations in Spitsbergen, Greenland, Sweden, Switzerland, Japan, Tenerife, Australia and New Zealand. These measurements are backed up by satellite observations and model simulations.
Professor Peter Bernath, from the University of York, who was also part of the international team of scientists, added: “Atmospheric variability and perhaps climate change can significantly modify the path towards full recovery and, ultimately, it will be a bumpy ride rather than a smooth evolution.
“The recovery of ozone-depleting chemicals in the atmosphere is a slow process and will take many decades. During this time the ozone layer remains vulnerable.”
Further information
The study was led by the University of Leige, Belgium, and involved scientists from Australia, Canada, Germany, Japan, New Zealand, the UK, and the USA.
The research conducted at Leeds received funding from the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC).
Professor Martyn Chipperfield is available for interview. Please contact Sarah Reed, Press Officer at the University of Leeds, on 0113 34 34196 or email s.j.reed@leeds.ac.uk.
The paper, ‘Recent Northern Hemisphere stratospheric HCl increase due to atmospheric circulation changes’ is published in Nature on 6 November 2014.
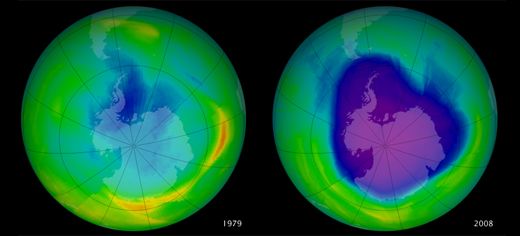
The image shows the Antarctic ozone hole, shown in blue and dark purple, in 1979 (left) and 2008 (right). Credit: NASA’s Earth Observatory